Vacuum Pump Used To Create A Partial Vacuum Within A Closed System By Removing Gas Or Air Molecules
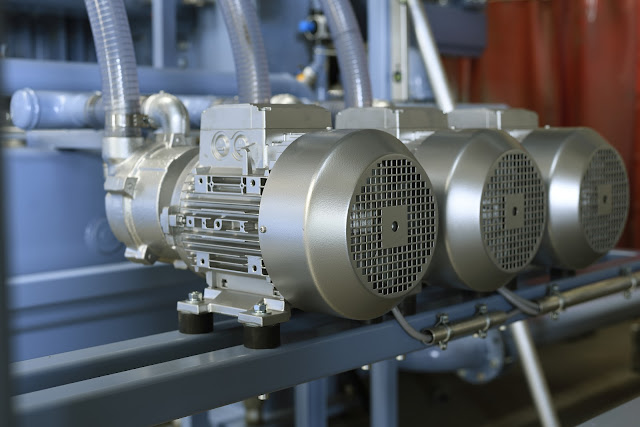 |
| Vacuum Pump |
A
Vacuum Pump is a mechanical device
used to create a partial vacuum within a closed system by removing gas or air
molecules from the enclosed space. It finds applications in scientific
research, and everyday life. The fundamental principle behind its operation is
to decrease the pressure within a chamber or container below the atmospheric
pressure, thus allowing the removal of gases or creating a space devoid of air.
The
history of pumps dates back to the mid-17th century when the first rudimentary
pumps were developed to assist in scientific experiments. However, significant
advancements were made during the 19th and 20th centuries, leading to the
development of more efficient and versatile pumps.
According To Coherent Market Insights,
The Vacuum
Pump Market Was Estimated At USD 6.07 Million In 2022, And From That Year
To 2030, It Is Predicted To Increase At A CAGR Of 7.29%.
One
of the earliest and simplest Vacuum Pump is the manual suction pump, known as the
"suction pump." These pumps rely on human effort to create a vacuum
by pulling a handle or using a piston to lower the pressure inside a chamber.
While effective for certain applications, they have limited applications and
are mostly replaced by more advanced technologies today.
Modern
vacuum pumps come in various types, each suited for specific applications. One
of the most common types is the "rotary vane pump," which uses
rotating vanes to compress gas and move it out of the pump. These pumps are
widely used in applications such as refrigeration, air conditioning, and
automotive systems.
Another
important type is the "diaphragm pump." This pump utilizes a flexible
diaphragm to create a vacuum by alternately expanding and contracting the space
inside the pump chamber. Diaphragm pumps are oil-free and are commonly employed
in laboratories and medical devices.
For
applications requiring a high level of vacuum, "diffusion pumps" are
used. These pumps work on the principle of diffusion, where gas molecules are
directed toward the outlet by a high-speed jet of vaporized oil or metal.
Diffusion pumps are essential in vacuum deposition processes and manufacturing
semiconductors.
Other
types of Vacuum Pump include
"scroll pumps," which use two interleaved spiral scrolls to compress
gas, and "turbomolecular pumps," which achieve high vacuum levels by
utilizing rapidly spinning blades to propel gas molecules out of the system.
Mechanical Pump
Seals are specialized
components used in pumps to prevent leakage of fluid along the rotating shaft.
Consisting of sealing faces and a spring mechanism, these pump seals provide a
secure barrier, maintaining fluid containment and minimizing energy losses
during pump operation.
Vacuum Pump has found widespread use in scientific research and
laboratories. They are crucial in creating controlled environments for
experiments, handling delicate samples, and enabling techniques like
freeze-drying. In the medical field, vacuum are used in various applications,
including suction devices during surgical procedures and vacuum-assisted wound
healing.


Comments
Post a Comment